What is Infected Hair Follicle?
Table of Contents
Folliculitis or infected hair follicles require immediate treatment if it does not heal on its own. This condition is characterised by the inflammation of the hair follicle.
A follicle is a tiny pouch in the body from which hair grows. Any part of your body can have folliculitis where there is hair growth. Most common areas where hair follicle become infected are:
- Beard
- Arms
- Back
- Buttock
- Legs
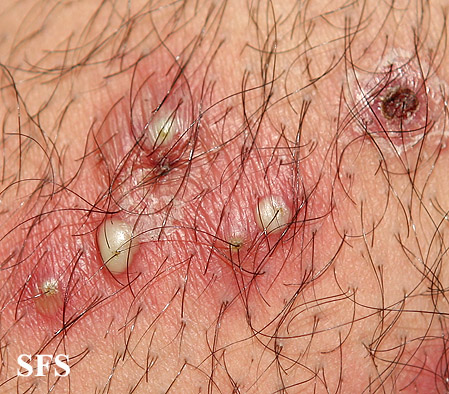
Infected hair follicles appear as red, point like bumps and there is also a presence of a dot of pus at the tip. From young babies to seniors, this disease can impact anyone. These smooth red bumps which are tiny in size are seen on parts of the body such as the face, legs, back, chest and scalp around the follicle.
Causes: Why Do You Get Infected Hair Follicles?
Bacteria/Fungus
Infection in the follicle of the hair can be caused by bacteria, yeast or other types of fungus.
Follicle Damage
When the hair follicle gets damaged, it is likely to be infected. This can be caused if clothes rub against the follicle or shaving irritates it.
Blockage
Irritation and infection from blockage can also occur as a result of sweat, machine oils or wearing cosmetic formulations.
Who is at Risk?
You are at greater risk of developing an infected hair follicle if:
- Your immunity is weak or lowered due to disease
- You have an infected surgical cut, scrape or wound
- Your use substances like cocoa butter and creosote which cause blockage or irritation
- Tubs, pools or jacuzzis with poor hygiene and lack of chlorine are used
- Tight clothing is worn
Depending on the degree of follicle infected and damaged, folliculitis can be deep or superficial. Most of the skin is covered with tiny hairs growing out of the follicles. Many hair follicles can get affected developing into small, pus-filled pimples looking like a small rounded, red spot.
Types of Folliculitis
Most cases of folliculitis occur due to infection by a type of bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). This generally occurs in the nose of people without harming them but can damage hair follicles. Friction or shaving also causes folliculitis.
Using a steroid cream on the face can also cause this condition. Another common cause is hyperhidrosis or overactivity of the sweat glands.
Folliculitis can occur on hair-bearing skin in any region of the body. The most common type of infected hair follicle are:
- Sycosis barbae
- Hot tub folliculitis
- Gram negative folliculitis
- Pseudo-folliculitis
Sycosis Barbae
Photo By: Andrew Magill/CC ByThis is a medical term denoting long standing or chronic folliculitis. This is generally in the beard area of males and it can also affect the upper lip.
Many pustules develop in the hair follicles and skin is painful and crusted with burning and itching when shaved or touched.
Hot Tub Folliculitis
In keeping with the name, this affects people who use a lot of hot tubs. This encourages a particular bacterium called Pseudomonas app. to grow. This is more likely to happen if the water is not chlorinated to stay clean.
Bathing in bacteria like these can cause infected hair follicles. Proper maintenance of hot tubs is the only preventing. Showering after the hot tub does not prevent the problem.
Gram Negative Folliculitis
This type of folliculitis occurs after the treatment of pimples with antibiotic. In this type of folliculitis, different bacteria are involved. Gram-negative stands for the stain in the lab to identify these bacteria germs.
Pseudo Folliculitis
This problem is caused due to ingrowing hairs and is common in people of Afro-Caribbean descent or those with curly hair. Hairs curled around and growing back into the skin are ingrowing hairs.
This occurs in people where the hair bends and enters the skin and is also caused by dead cells blocking hair growth. Scratching or picking the pimple that results from ingrowing hair can cause scarring.
Symptoms
- Infected hair follicle looks like red pimples with hair in the center of each one.
- Pimples also experience itching and a burning sensation
- They are filled with pus
- When they break open, they drain pus, blood or both
- Hot tub folliculitis is also accompanied by mild fever and upset stomach, but it generally goes away in less than a fortnight on its own without treatment.
How is Folliculitis Diagnosed?
Photo By: Wikipedia/CC BYDoctors check the skin and ask questions about recent activities and state of health. Tests may be done to check if it is an infected hair follicle or impetigo or heat rash.
Sample testing of fluid in a pimple or tissue can inform the doctor about what is causing the infection.
Folliculitis is an infection caused where tiny pus filled spots occur at the base of the hair.
Treatment and Prevention
Measures include avoiding factors that lead to this condition. For example, the right direction of hair growth in shaving is a must. Folliculitis may go away on its own. Exposure to fresh air can also cure the condition. Tight clothing aggravates it. Don’t share towels or razors when you have this condition.
Mild Cases
Mild cases of infected hair follicle go away on their own. Moisturises with emollient containing anti bacterial agent like Dermol or Emulsiderm might help. This improves the condition of the skin and soothes it. It also helps the infected hair follicle to clear quickly and reduce chances of symptoms worsening.
Localised Infected Hair Follicle
Localised folliculitis can be treated through antibiotic cream which can be applied 3-4 times in a day on the affected parts of your body.
Severe Case/Chronic Case
Picture By: AmazonFor severe or chronic cases, antibiotic tablets may be prescribed by your GP.
Recurrent folliculitis where gaps between episodes gets shorter may result in chronic form of this condition.
Skin swab will be taken and if S. aureus is confirmed as the cause, the aim will be to destroy the staphylococci through antibiotic tablets and antibiotic nasal cream (because this bacterium is found in the nose to begin with).
Finally antiseptic skin wash and shower gel may be needed and repeated swab testing may be done to assess if the condition is cured.
Prevention
Prevention is certainly better than cure and taking steps like not sharing towels, avoiding unchlorinated pools and tubs, not shaving the wrong way and avoiding tight clothes which cause friction and sweating may be advisable.
Maintain proper hygiene and ensure that you do not shower without a mild soap. Use hot compresses for immediate relief for this condition.
An infected hair follicle is more than a condition. It is a problem, especially because of the disfiguration and pain it causes.
Conclusion
Heed the possible complications and go for treatment, but remember that maintaining healthy hair follicles is all about avoiding germ ridden and infected areas in the first place. Take preventive steps today for a healthier you and reap the benefits of elimination of folliculitis.