Chickenpox: Definition and Clinical Picture
Table of Contents
Chickenpox (varicella) is a viral illness where an itchy red rash is a chief symptom. Since vaccination became widely used to prevent this condition from the 1990s onward, it has become rare now. While chickenpox is usually mild in children, adults experience serious complications such as bacterial pneumonia.
Chickenpox is a contagious and highly infectious disease. While those younger than 15 years of age are most likely to get it, teens and adults are also prone to this condition. Chickenpox is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with affected persons and lack of vaccination.
According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, chickenpox was widely prevalent, with approximately 3m people getting the disease each year, before the introduction of the vaccine in the US in 1995. CDC estimates that chickenpox cases have fallen by nearly eighty percent.
Another fundamental fact about chickenpox is that those who have this disease get lifetime immunity once they recover. However, the virus can lie dormant in the system and lead to shingles in later life.
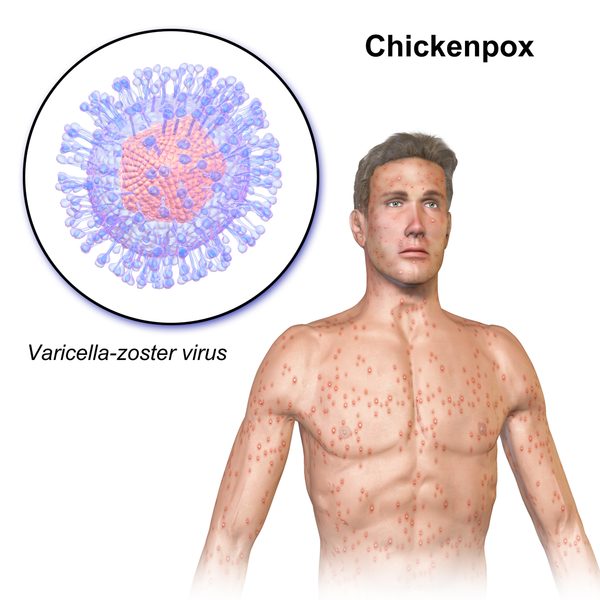
Chickenpox in pregnant women may associate with serious congenital disabilities in the child. Confirming their immunity with a blood test is often advised for women considering pregnancy. The varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox. Varicella-zoster virus known as varicella in some parts of the world as a result of this.
A blister type rash develops as a consequence of this disease, with a total of 250 to 500 such blisters forming in the final stage of the disease. Pox marks generally heal without scarring. This is an airborne disease and spreads through contact with the infected person. A person is contagious two days before the rash appears and continues to be so for another 4-5 day period. When the lesion has crusted over, they can no longer infect another person. Those with weak immune systems may be contagious for longer. Varicella rash appears 10 to 21 days after the virus has infected the patient.
Causes and Complications
Chickenpox is caused by VZV and persons can become infected by those who are contagious. Chickenpox is a highly infectious disease- close to 90 percent of those without chickenpox who have not been vaccinated are prone to this viral disease.
Chickenpox spreads the same way that other viral diseases do. Droplets of secretion or discharge from the nose and the mouth of the infected person are released through coughing and sneezing. These are inhaled by those around them and if the contaminated discharge lands on an object, it can become a source of infection too.
Chickenpox from Shingles
Chickenpox can also be contracted from a person with shingles though infection the other way round is not possible. People who never had this disease or were not vaccinated can develop chickenpox due to this reason.
Chickenpox: Onset and Contagion
The onset of symptoms takes place 7-21 days after exposure to the virus, and the disease is most infectious a day after the rash appears, up to 7 days or till the rash forms scabs and dries up. Chickenpox lasts 5-7 days. Chickenpox virus spreads easily when the infected person’s blisters are itching and break open quite easily. This can contaminate the open surfaces or tangible objects and the virus may be transferred by touching the object or the surface, and then your face.
The virus infects through millions of tiny droplets that come out when the infected person sneezes or coughs. The incubation period is generally around 14 days, but it can range from 7-21 days.
Chickenpox: Risks
Chickenpox caused by VZV can spread very quickly, and the virus is transmitted by direct contact with the rash or by droplets dispersed through coughing and sneezing. Risk of catching this disease is higher:
- If the patient has not had chickenpox earlier
- If he or she has not been vaccinated for chickenpox
- He/she resides with infected children/people
Most people who have chickenpox or have been vaccinated against it are immune to it. Few people get chickenpox more than once. Few blisters and mild or no fever is the feature of this disease when it recurs, and symptoms are milder.
Complications
While children recover from chickenpox without any issues, illness can be severe for pregnant ladies, newborns from those who have not been vaccinated, and those who did not have the virus before. This includes teen, adults, people with impaired immunity, and those infected with eczema.
People with serious complications may need to visit the hospital. Chickenpox can lead to hospitalization and death in certain cases. But with the introduction of the vaccine, chances of this complication occurring have lessened considerably.
Photo By: Johnny McCullagh/CC BYAccording to CDC, complications associated with chickenpox include:
- Joint diseases
- Dehydration
- Pneumonia
- Bleeding issues
- Infection/inflammation of the brain- Encephalitis, Cerebellar Ataxia
- Bone infections
- Bacterial infection of skin
- Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Soft Tissues in Children including Strep A infections
- Pregnant ladies who have never had chickenpox need to be careful as well as those vulnerable to complications including infants, teens, adults and those with immune system deficiencies
- Bloodstream infections/sepsis
Beginnings of Disease and Transmission
A typical symptom of chickenpox includes a rash that itches, fluid based blisters and eventual scabs. The rash may show up in the face first followed by the chest and the back.
The rash then spreads to the rest of the human body including lower extremities, mouth, and eyelids.
The disease takes one week for the blisters to change into scabs. Typical symptoms that occur a couple of days before the rash include:
- Fever
- Loss of Appetite
- Tiredness
- Headache
Complications from chickenpox do not occur in healthy people. Those with pre-existing disease conditions like HIV/AIDS or cancer and those with transplants or on chemotherapy or certain medications may experience complications. The complications resulting from this disease include Group A streptococcal infections and sepsis as well as dehydration, so care needs to be taken on these fronts. The VZV virus is related to the herpes virus.
Stages of the Infection
There are three stages.
First stage
This starts with the appearance of little, itchy bumps
Second Stage
Here the bumps turn into blisters filled with fluid.
Final stage
During this phase, the scabbing over of the bumps appears. Additionally, itchy scabs and fever, headache, dry cough and loss of appetite follow.
Beginning Phase
During the start of the symptoms, the following signs may be observed:
- Fever
- Feeling of malaise
- Aching muscles
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
A common sign of chickenpox is an itchy rash the severity of which varies considerably. While some patients may have a few spots, others are covered all over the body. Spots appear inc clusters on upper extremities, limbs, chest, stomach and under the arms.
These red spots itch a lot initially and then develop into spots with blisters atop them. Within two days, the blisters start drying out as a crust develops. In another ten days, the crust falls off. Spots can appear inside the mouth, in the palm of the hand and other places. During the complete cycle, new waves of spots can also appear.
Transmission
A person with chickenpox can spread the disease within a couple of days before the rash develops till all their chickenpox blisters have turned into scabs within 5 to 7 days. It takes two weeks (from 10 to around twenty-one days) after exposure to chickenpox and/or shingles for a person to develop this disease.
This communicable disease can be transmitted through droplets from coughing or sneezing by the infected person. Contact with the infected person can also lead to the spread of this disease.
Treatment of Chickenpox
Prevention
Photo By: AmazonPreventing chickenpox is only possible if you get a vaccine. Two doses of vaccine are given to the person to safeguard against this disease. This vaccine is safe and people with it do not get chickenpox usually. Even if by some rare chance they do, the chickenpox symptoms are few and very mild.
Treatment at Home
To relieve the symptoms at home and prevent further deterioration like skin infections, rubbing the calamine lotion and use of colloidal oatmeal bathings can help to relieve the itching. Fingernails need to be trimmed short to prevent itching related blisters due to scratching.
As far as OTC medication is concerned, you need to use non-aspirin medications like acetaminophen. Don’t use aspirin-related medicines because this causes Reyes’ syndrome, a severe liver disease which can result in death.
When Do You Call The Doctor?
You need to call the doctor if:
- Person is severely affected
- He/she is less than 1 years old
- He/ she is older than 12 years of age
- Suffers from weakened immunity
- Has fever rising above 102 degrees F
- Pregnant
- A Severe cough and some abdominal pain
- Has fever that lasts longer than 4 days
- Extreme illness
- Weakness and confusion getting up
- Stiff neck
- Difficulty breathing
- Rash and bleeding/bruising
- Rashes in the body become warm or tender and leak pus indicating bacterial infection
Healthcare provider can guide you on the treatment options. Chickenpox is generally diagnosed by visible symptoms. Doctoral checks for fever and may call for a blood test. Tests may also be recommended for pregnant mothers, newborns, people about to receive organ transplants and those with HIV-AIDS.
Two main types of testing are there:
- Antibody testing
- Viral testing
Antibody testing looks for an antibody IgM which is released in response to an infection.
Viral testing involves collecting fluids from the blisters and testing the DNA on a sample or using a microscope to visualize the infection
Anti-viral medication Acyclovir is used for chickenpox treatment. This medicine works best around 24 hours after the rash begins. Other anti-viral medications working against chickenpox include famciclovir and valacyclovir.
Conclusion
Chickenpox may no longer be a threat, thanks to the vaccination, but it is a problem for those who suffer from weak immunity systems or preexisting medical conditions. Check with your healthcare practitioner if you need hospitalization and take plenty of fluids. Medical science has advanced to a point where people can follow precautions too. Choose prevention and prompt treatment, if you develop this condition.