What is COPD?
Table of Contents
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/COPD refers to a set of lung diseases that make it harder to empty air out of the lungs. This can lead to fatigue or shortness of breath.
Conditions that come under COPD include chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
COPD is a group of diseases where coughing and sputum production increase and signs of whether this is due to smoking are measured through a test known as spirometry which sees if your airways are blocked or not.
Diagnosis
Based on the report of symptoms and test results, a doctor may diagnose you are having COPD. Remember to share medical history, smoking practices (if any), exposure to chemicals and pollutants and the period since the time symptoms have emerged.
Causes of COPD
COPD can be caused by many reasons. The most well known and common one is smoking. Even second-hand smoke causes COPD, so non-smokers are not immune. Irritating particles if inhaled can cause the bronchi (bronchial tubes) to generate more mucus than usual.
It also causes the tubes to swell and increased mucus raises the frequency of coughing. COPD can develop regardless of whether short amounts of smoke are inhaled over a period or vice versa.
Genetic and environmental factors can lead to COPD as well. Exposure to dust,chemicals or pollutants can also exacerbate chances of developing COPD.
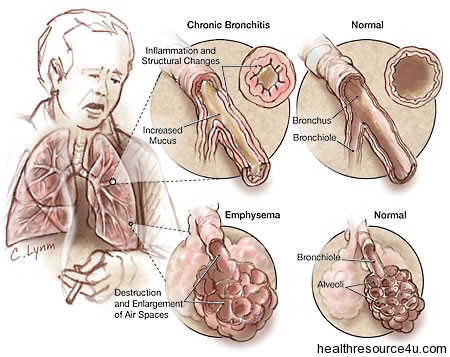
Common COPD Conditions
Chronic Bronchitis
This is a constant swelling and irritability of breathing tubes resulting in increased phlegm. Tubes are called bronchi/bronchioles. Chronic bronchitis is diagnosed when a cough and mucus have been reported for over 3 months in 2 years , and no other lung condition like asthma is the cause.
This COPD condition has airways obstruction as swelling and more mucus cause the breathing tubes to become blocked and choked. Narrowing of airways also prevents air from reaching the lungs.
Emphysema
This is a disease that concerns the air sacs or alveoli of the lung. With over 300 million such air sacs, emphysema is a condition which is tough to cope with as the walls of the alveoli become damaged.
This causes the air sac to become more like a bag, easy to blow up but tough to exhale or breathe out. Getting air into the lungs is as tough as getting it out in this condition.
In this COPD condition, breathing tubes collapse because air sac walls are damaged. The alveoli walls generally hold the breathing tubes open as one exhales.
Chronic in COPD means that you will have this condition for life. COPD also worsens over time. While you cannot undo the damage, you can manage it and prevent the worsening of symptoms.
Symptoms of COPD
The chief symptoms of COPD are:
- Chronic cough
- Excess Mucus or Phlegm discharge
- Breathlessness/ Shortness of breath which worsens with activity
As COPD worsens, even simple things like eating and exercise become tough as people begin to lose weight and become weaker.
Symptoms can flare up and worsen in what is called COPD exacerbation. The longer you have the condition, the more likely it is that the flare ups will come.
COPD also causes breathlessness, shortness of breath, overproduction of mucus or sputum and fatigue or tiredness. When the symptoms first appear, people often do not realise they have COPD thinking they are just out of shape or it’s a smoker’s cough.
Coughing
A cough is a reaction of the airways to remove mucus or protect airways from inhaled chemicals and pollutants. People with certain other conditions may also have a cough such as common cold or even hernia. Coughing that causes people to pass out or be ceaseless should be reported to the doctor.
Dyspnea
This is shortness of breath or breathlessness and it is a sure shot symptom of COPD. Bear in mind that activity induced breathlessness may be normal in COPD and so exercising should be carried out as this does not further damage the lungs.
But leading an active life with COPD is not easy. Pulmonary rehab programs which train people how to cope with shortness of breath can prove helpful.
Mucus Production
Sputum or phlegm production from the lungs is different from sinus drainage. Airways produce several ounces of sputum per day and when lungs are bothered by irritants, this increases.
Chronic irritation also damaged the natural cleaning system provided by cilia or hairlike structures in the airways. To treat excessive sputum production, generally antibiotics, expectorants, and mucolytics are used. But COPD patients rely on drinking non-dehydrating liquids like water and juice.
Medications are only used when natural methods do not work.
Treatment of COPD
While there is no known cure for COPD, the treatment, and management of symptoms can make you more active and slow down the chances of symptoms advancing or worsening.
Goals of COPD treatment
This includes lowering symptoms, slowing the disease, increasing the ability to stay active, improving overall health and preventing medical complications.
Lifestyle Changes
Leave smoking…it can save your life. Besides quitting smoking, patients should also avoid second-hand smoke and toxic substances that are inhaled such as dust and chemical particles. Use support groups to quit smoking.
Quitting smoking is the most important step you can take to treat COPD. Talk with your doctor about programs and products that can help you quit. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute offers informative details on how to quit smoking.
Change your eating plan as symptoms like shortness or breath and fatigue make it tough to have heavy meals. Check with your practitioner about having small, more frequent meals and vitamin or nutritional supplements. Resting before eating and picking a physical activity or exercises to strengthen your lungs and muscles can also make you feel better.
Medicines
This include:
- Bronchodilators
- Combined Bronchodilators Plus Glucocorticosteroids
While bronchodilators relax muscles and ease breathing through airways through a device called the inhaler, a inhaled steroid may also be prescribed for those with severe COPD who experience flare-ups.
Various vaccines such as flu shots, pneumococcal vaccine lower the risk for COPD conditions to aggravate into life-threatening states.
Medical Treatment
This includes pulmonary rehabilitation and oxygen therapy. The former includes exercise, disease management training and nutritional as well as mental health support and the rehab team can comprise multiple types of healthcare practitioners. Nasal prongs or mask can also be used to provide more oxygen to the COPD patient.
Surgery might help those with severe symptoms and includes:
- Lung volume reduction surgery
- Bullectomy
- Lung transplant
Conclusion
Severe COPD can be life-threatening. Patients should seek medical advice and counselling to avoid worsening of symptoms. Wellness lies in an effective management of symptoms through a combination of nutrition, exercise, and medical treatment.