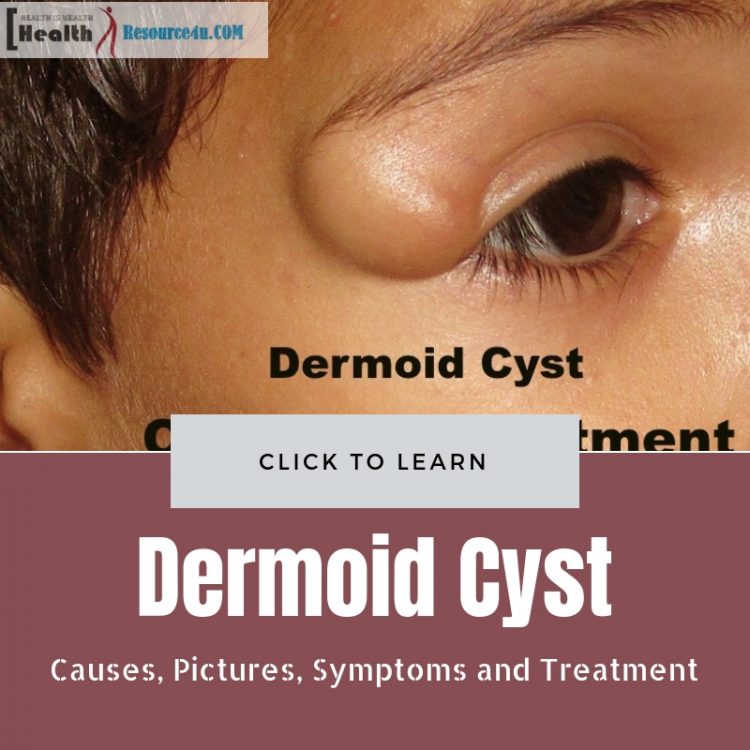
Dermoid cysts are pockets or holes beneath the human skin. Such cysts have tissue generally located in external skin layers. Dermoid cysts can have oil, sweat glands, or even hair follicles. The oil and sweat buildup within them increase the cyst’s size. Dermoid cysts can occur at birth or shortly after it. Besides congenital cysts, these skin formations can also happen years later. Dermoid cysts are located on the face, neck or head, generally. However, they can also occur in other parts of the body. Dermoid cysts are also called teratoma because they refer to developmentally advanced tissues in an array. Dermoid cysts comprise skin, sweat glands, hair follicles and other components including clumps of extended hair strands, blood, fat, nail, bone, sebum, tooth, eyes, cartilage, or even thyroid tissues.
Such cysts grow slowly. They contain mature tissue. This cystic teratoma is always benign, in most cases. When a dermoid cyst is malignant, a squamous cell cancer can develop in older adults. Infants or kids generally display an endodermal sinus tumor. Dermoid cysts are also called dermal or epidermal inclusion cysts or epidermoid cysts. They are mostly found in the upper chest, besides the face, neck, and head. These cysts are common orbital or preorbital tumors that generally occur in children. They grow gradually and are lined by oil and skin cells. Dermoid cysts can describe skin lined cysts under the skin, cysts including follicles or deeper cysts containing oil, skin and hair follicles. Dermoid cysts represent complex tumors found in female ovaries called ovarian teratomas.
What is a Dermoid Cyst?
Table of Contents
To answer this, we can say it is a sac-like growth present mostly since birth in children or adults. It contains structures that can be found within or on the skin. Dermoid cysts generally do not become tender, unless they rupture. They are located on the face, within the skull, the base of the back and the ovaries. Superficial dermoid cysts on the face can be easily removed sans complications. Rarer dermoid cysts require special techniques and training.
Rare dermoid cysts take place in 4 key areas:
Cysts in the brain: Dermoid cysts in your brain are rare, but they can occur. A neurosurgeon can remove them if they trigger problems.
Cysts in the nasal sinus: These are rare, too. Removal of such cysts can entail complications.
Cysts in the ovary: Such cysts are found in women during reproductive years. They lead to infection and can rupture. Such cysts may also cause twisting/torsion and cancer. Such cysts must be removed either through surgery or laparoscopy (a form of medicine that is minimally invasive).
Cysts in the spinal cord: These rare cysts are connected to the skin’s surface by a sinus tract, a close connection from a skin surface. These cysts are likely to become infected. Removal is an intricate procedure, therefore incomplete. The outcome, however, is exceptional.
Thus, dermoid cysts are located in an enclosed sac near the skin’s surface. These generally form during the baby’s fetal development. Cysts contain hair follicles, skin tissue, and glands secreting oil and sweat. Such glands produce these substances, triggering the growth of the cysts.
Dermoid cysts are relatively common. Though they are harmless, they require surgery, though. They cannot get better with time on their own.
Types of Dermoid Cysts
Dermoid cysts norm within the skin’s surface. Some of these cysts can easily be noticed at birth. Others are located deep within the body, and can only be detected later in life.
Dermoid cysts can be differentiated based on their location in the body. The most common types are listed below:
Preorbital
Such dermoid cysts are formed near the right brow’s right side or left brow’s left area. Such cysts are congenital. They may not appear evident for months or years post the birth, however. Symptoms in question are minor. There is limited risk to the vision or health of the child. If the cyst is infected, prompt treatment and surgery are vital.
Ovarian
This kind of cyst forms within or on an ovary. Such ovarian cysts pertain to menstruation. These dermoid cysts may form in the ovary, but have no link with its function. Ovarian dermoid cysts also develop before birth. Women may have undiscovered dermoid cysts in the ovary. That is why a pelvic exam is crucial.
Spinal
This tumor is a benign or harmless cyst. It forms on the spinal cord. It does not spread. It may present zero symptoms and cause no harm. But while the cyst appears harmless, it can create a problem, when it presses against spinal nerves or the spine. Due to this reason, it should ideally be surgically removed.
Characteristic Features of Dermoid Cysts
Wherever they are located, such cysts are generally benign. They are a form of tumor referred to as teratoma, as per the National Cancer Institute. These cysts usually are non-cancerous. Dermoid cysts are unique because they originate from germ cells. Given these are reproductive cells, they can refer to egg or sperm cells. Cells differentiate and divide during embryonic development to form this cyst. These cells have the stuff of other cells in the DNA, as they make embryos that progress to fetuses and babies. Like other tumors, these cysts form when cells develop abnormally.
Dermoid cysts form when germ cells get stuck in the wrong place while fusing. These wayward cells enter the wrong location and keep thriving. In healthy cell development, cells grow and divide until an internal signal is received. When such mechanisms go wrong, the body does not receive the message, and cell growth keeps going. Consequently, tumors form. Such cysts can remain undiscovered for years. The way it appears depends on where it is located. Sometimes, even these harmless cysts can cause trouble. Large dermoid cysts in the neck cause pressure on the throat and surrounding structures, impacting breathing and swallowing. Brain or spinal cord dermoid cysts can trigger weakness or headaches. Dermoid ovarian cysts can create torsion, resulting in pain, nausea, and vomiting. Ovarian dermoid cysts also rupture easily, triggering bleeding and pain. While a dermoid cyst may be harmless, it is generally removed to prevent issues down the line.
Even when it is issueless, the cyst grows continuously. It releases oil and skin cell debris. If bacteria get in, the cyst can be infected. Once a cyst expands or becomes infected, removal is hard. So, doctors generally recommend surgical removal to prevent complications ahead.
However, most of this depends on the cyst size and a cost-benefit analysis of removal.
Symptoms
A lot of dermoid cysts do not cause symptoms. This reason is why they remain undetected for such a long time, and develop into complications, only after cysts are infectious or large-sized. What symptoms are present depend on the location?
Preorbital
These dermoid cysts are present near the surface of the skin. They tend to swell up. The skin develops a yellow-type tint. Infected cysts become swollen and red. If the cysts burst, they lead to infection. Areas surrounding the eye can swell up, in case of facial cysts.
Ovarian
In case the cyst enlarges, pain may be felt in pelvic regions. The pain will be felt on the cyst’s side. The pain can be severe during menstruation.
Spinal
For such cysts, trouble begins when the growth compresses either the spinal cord or nerves. The size and location determine which body nerves are impacted. Symptoms, when they do occur, can include problems in walking, weakness, and sensations of tingling in the legs and arm. Incontinence may also be noted.
General Symptoms
A dermoid cyst appears like a lump beneath the skin. The skin above the bump can be easily moved. The lump can be skin-colored or blueish. Dermoid cysts can be much like other health conditions when it comes to symptoms. Outside of the eye, dermoid cysts could be painless masses. Only when they are near the eye can they cause pain and vision issues. Dermoid cysts can be conceived as skin trapped in impacted areas at the time of fetal development. While skin generally produces oil on the surface, shedding skin cells, a dermoid cyst emerges as a skin bubble trapped inside out. Or It can be trapped beneath the skin, as well. In such cases, trapped skin leads to oil and skin cells enlarging, causing the cyst to expand. If the dermoid cyst within the bone such as the skull grows, holes in the bone extend too.
Causes
Dermoid cysts are sometimes seen in babies not yet born. It is not clear why some fetal or embryonic development processes lead to dermoid cysts.
Preorbital
Such a dermoid cyst forms, when skin layers fail to grow correctly. Skin cells and other material collected in a skin surface sac. As glands continue to generate fluids, the cyst increases in size.
Ovarian
Ovarian dermoid cysts are growing on the uterus form during embryonic development. The cyst includes skin cells, tissues, and glands that should not be on the inner organ, but instead on the skin’s layers.
Spinal
These dermoid cysts are caused commonly due to spinal dysraphism. This takes place right at the start of embryonic development. Parts of the neural tube don’t close, so the cyst forms. This tube is a cell collection that becomes the spinal cord and the brain in a fully mature adult.
Causes: Overview
Dermoid cysts occur when skin structures or skin or both are trapped in fetal development. The cell walls resemble outer skin and can contain multiple structures.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing this cyst when it is preorbital or near the neck or on the chest requires a physical exam. Doctors cam also move the cyst beneath the skin to see its shape and size. Imaging tests can point if the cyst is in a vulnerable area like the carotid artery. Doctors can see where the cyst is present. Also, the risk of damage to sensitive areas is assessed. Imaging tests used to range across CT and MRI scans. CT scans use specialized X-rays. Using computer equipment, they present 3-D layered views of body tissues. MRI scans, on the other hand, deploy magnetic fields or radio waves to come up with detailed body images.
MRI or CT scans can also diagnose spinal cysts. Before treating spinal dermoid cysts, doctors may check which nerves this tumor is impinging on. Pelvic exams can reveal the presence of ovarian cysts of this type. Imaging tests like pelvic ultrasounds can be used. Such an ultrasound creates images using sound waves. A transducer or wand-type device rubbed across the lower abs creates screen images.
Doctors may also suggest the use of transvaginal ultrasounds. The want is inserted within the vagina. Like the other ultrasound, the wand’s sound waves create images.
Your doctor may also use a transvaginal ultrasound. During this test, your doctor will insert a wand into the vagina. Like with the pelvic ultrasound, images will be created using sound waves emitted from the wand.
Treatment
Contact your doctor if cysts are swollen, painful, growing, changing color, or require removal for medical or cosmetic reasons. Removing such a cyst is not an ER procedure. However, immediate care and treatment are essential if the cyst inflames, causes fever or pain or even ruptures.
Before the removal of these dermoid cysts on the face, be evident that such cysts which are firm and pain-free might ache after rupturing. Dermoid cysts only extend more than the skin into structures like face cavity or orbit in rare chances. Some doctors may recommend imaging studies to examine this. Decisions to use tests depend on how deep the cyst is and the risks involved.
Self-removal of the cysts is not recommended. Cysts grow back if not completely operated. Chances of bleeding, infection, and complications rise for those using their methods to remove cysts. Lay patients may not be able to check if it is harmless or malignant growth. For removing the dermoid cyst, doctors clean the area it is located in, inject localized anesthesia and remove the cyst using incisions directly above it.
Surgery
Specifically, the only option for the treatment of severe dermoid cysts is surgery. Many key factors are considered, especially in pediatric surgery. These include symptoms, medical history, presence or risk of infection, tolerance, or aversion for operation and post-surgical medicines. Cyst severity and patient/caregiver preference must also be considered.
Surgical excision is used irrespective of cyst location. The average period for surgery varies. Surgery needs to be carefully performed in individual patients, as the content of the cyst spreads to anatomic structures or surrounding tissues. This is more so in bacterial cyst infection. The spread of disease can cause body reactions due to foreign pathogens or severe complications.
Pre-Surgery
You should follow the doctor’s directions before surgery. They can inform you whether you need to stop taking medication or eating before surgery. As general anesthesia is used, transport arrangements should be made before surgery.
At the Time of Surgery
For surgery involving the preorbital dermoid cyst, small eyebrow or hairline incisions can conceal scars. The cyst is removed. The entire process takes half an hour, by most estimates. For ovarian cysts, surgery is complicated. Sometimes, it even requires ovary removal or ovarian cystectomy. When the cyst is large, or the ovary is damaged, both should be removed at the same time. Microsurgery is used for spinal cysts. Small instruments are used, and the patient is generally in the operating theater for this surgery. Doctors open the dura or thin spinal covering to get to the cyst. Nerve functions are regulated. This is a complicated procedure.
Post-Surgery
Certain cyst surgeries are carried out as an outpatient. This means you can recover and go home on the very same day. Spinal surgeries could require an overnight stay to detect complications. If the spinal cyst is firmly attached to the nerves or spine, much of the cyst will be removed. Remaining cysts are carefully monitored following this. Post-surgical recovery may take place 2-3 weeks, based on cyst location.
Previously surgery was the only way out for dermoid cysts. It was especially complicated for bone cysts as opening access to the bone was followed by scraping or drilling dermoid cyst cells from the bone cavity. When cysts are on the forehead or in the skull, extensive incisions are needed. This is why minimally invasive procedures like drainage and ablation came about Dermoid cysts can be killed through drainage and ablation.
Cyst Ablation
Dermoid cyst ablation is a minimally invasive procedure. A plastic sleeve and small needle enter the cyst. It kills or ablates the cyst. Then, during healing, the body’s cleanup mechanisms remove the dead cyst cells, leaving a freckle-sized scar.
Dermoid cysts are generally drained before ablation. Cyst contents are released through a technique that thins oil and sebum particles using medical detergent. Permitting drainage of cyst, this procedure leads to cleaning and removal of the contents. Collapsed lining membrane or skin cells lining the cyst are ablated with a precise needle method called coblation. Then, ultrasound guidance requires the needle tip to be placed within the collapsed cyst. Plasma energy destroys the cysts’ cells.
Dermal ablation takes place in less than 60 minutes. The primary issue that can arise is overlying skin injury. That is why sterile fluid injections are used to lift the skin away from the coblation energy cloud, offering precise ablation of dermoid cyst capsules without adjoining skin injuries. Once the dermoid cyst’ ablation process completes, the cyst cells are removed. The body heals the area treated. In case the cyst is on the bone, the healing process ensures that new bone forms to replace defects caused due to cysts.
New bone healing after cyst ablation takes two to three months.
While untreated cysts of this kind are harmless, it all depends on the location. Further, dermoid cysts may rupture and infect adjacent tissues. Spinal dermoid cysts left uncured grow large enough to injure the spine or its nerves. So, they must be treated. The same holds for ovarian cysts.
As dermoid cysts are mostly congenital, they cannot develop later in life, generally. Though these cysts are harmless, the pros and cons of surgery should be clarified. In several cases, cyst removal surgery can be carried out without complications or long-term issues. Removing the cyst eliminates chances of rupture and infection.
Laparoscopy
Ovary dermoid cysts may be treated using laparoscopy, besides laparotomy. Diagnostic laparoscopy and transvaginal ultrasounds have made it easy to operate such cysts. Laparoscopy is generally preferred for ovarian cysts. However, it’s not without the risks. Chemical peritonitis can result from spilled and ruptured dermoid cysts.
Along with this, intraperitoneal tumor dissemination can occur if dermoid cysts are malignant. Content spillage due to cyst rupture can be deadly. So, it is essential to remove such cysts. Laparoscopy is cheaper than open surgery, and experienced laparoscopic surgeons can help in minimizing peritonitis through precautions.
Dermoid Cysts in Children
While dermoid cysts are congenital, they can occur in any part of the child’s body. The doctor diagnosis the cyst based on surrounding areas and appearance of the abnormal growth. Imaging tests may be required to see if cysts are linked to tissues in the neck and head. While treatment depends on age, general health, and symptoms, it is also a function of the cysts’ severity. Cysts can affect eyesight, damage bones, cause infections, or rupture. Apart from treatment site care, no activity risks follow ablation or surgery for children. Dermoid cysts can enlarge if left untreated. If there is rupture or injury, painful swelling, or infections result. Therefore, surgical removal is recommended.
Conclusion
Dermal conditions such as cysts are generally considered harmless, but these dermoid cysts can be complicated to treat. Choose a specialist or experienced surgeon for your treatment, especially if there are potential complications involved. Be careful about the condition, for though it appears harmless, it can trigger many problems as time progresses.