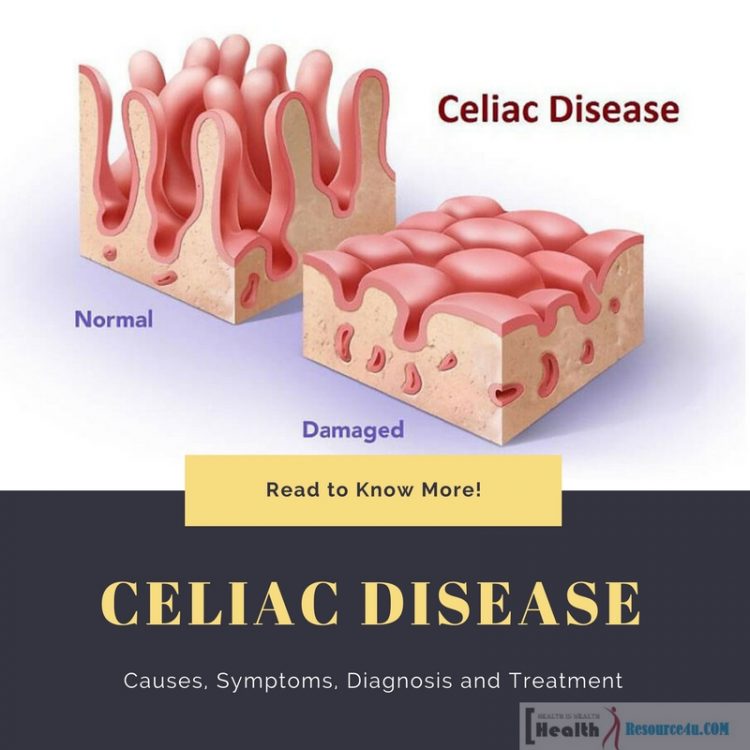
Lots of people prefer a gluten-free diet, but for those with Celiac disease, it’s hardly a matter of choice. Close to three million Americans have this autoimmune disease triggered when gluten is consumed. A substance found in rye, wheat, barley, and other grains, gluten is a complex protein. This protein makes dough elastic and is the reason bread has such a texture which is chewy. When people with celiac disease eat gluten-rich foods, the protein damages their body, specifically the villi which is a finger-like projection located along the small intestine walls.
Further, when the villi face injury, the small intestine cannot absorb nutrients from food effectively. This spurs undernourishment and leads to loss of density of the bone, infertility, and miscarriages. Celiac disease even leads to neurological diseases and certain forms of cancer at an advanced stage.
Celiac disease is tough to diagnose as it impacts persons differently. More than two hundred known Celiac disease symptoms take place in the digestive system or other body parts. While some people develop this disease during their childhood, others manifest it when they are adults. The cause for this disease is not known.
Certain patients with celiac disease lack symptoms, but still test positive on blood tests to diagnose and detect celiac disease. Some people with celiac disease are also likely to have no symptoms but still test positive. On the other hand, few others may have a negative indication in the blood test, but a positive intestinal biopsy. All persons with celiac disease cause long-term problems, whether or not symptoms are displayed.
Celiac Disease: Key Symptoms
Table of Contents
While this disease involves symptoms pertaining to the intestine and digestive systems, it can impact other body parts as well. Celiac disease has different symptomatology in adults and in children.
Symptoms in Children
Kids with celiac disease can undergo fatigue and irritability. Smaller than normal, these children may have late onset or delayed puberty. Other common symptoms include weight loss, abdominal bloating, vomiting, pain in the abs, constant constipation or diarrhea and pale, fat-rich, foul-smelling stool/discharge. Symptoms of pediatric Celiac disease are common in children and infants. The most common symptoms are abdominal pain and bloating. Weight loss is another common symptom.
Additionally, other common symptoms include delayed irritability and behavioral issues. Additionally, the dental enamel impacts the permanent teeth as well leading to delayed puberty and growth. Short stature, difficulty in growing tall or healthy are not the only problems. Kids with this disease may also suffer from Attention Deficit Hyperactivity/ADHD disorder.
Symptoms in Adults
Adults with Celiac disease may experience digestive symptoms. In many cases, symptoms may impact other parts of the body. These symptoms include iron-deficiency anemia, stiffness and joint pain, weakness and brittleness of bones, seizures, fatigue, disorders of the skin, tingling and numb sensations in the limbs and hands. Patients with this disease may also have pale sores in their mouth and loss of enamel or tooth discoloration. Irregular menstrual periods, miscarriage and infertility are some other symptoms.
Dermatitis herpetiformis is one of the many skin symptoms of this disease as well. It is an intense, itching skin rash composed of blisters and bumps. It can lead to a problematic rash on the glutes, knees, and elbows. This dermatitis condition affects 15 to 25% of those with celiac disease. Those who experience this form of celiac symptoms generally lack the digestive symptoms.
Symptoms tend to vary from one individual to another based on factors like length of time of breastfeeding as an infant, the age from which gluten-rich diet was consumed, the degree or percentage of the diet containing gluten and the severity of the intestinal damage.
Certain people with Celiac disease lack symptoms at all. They also develop long-term issues as a consequence of disease. Adults are less likely to have digestive and GI symptoms. Only one-third of the people experience diarrhea. Adults may also experience joint or bone pain, fatigue or iron deficiency anemia. Bone loss in the form of osteoporosis or osteopenia may also be experienced. Liver and biliary tract disorder include fatty liver, transaminitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis and much more. There are depression, anxiety, and peripheral neuropathy as well. This causes tingling, numbness, and pain in the feet and hands. There can also be seizures or migraines in those suffering from Celiac disease.
Other fertility symptoms include irregular menstruation, infertility, recurrent miscarriage and even canker sores in the mouth and itchy skin rash or dermatitis herpetiformis.
Classical Versus Non-Classical Forms of the Disease
As per the World Gastroenterologist Organization, Celiac disease can be divided into these two types namely classical and nonclassical.
The classical celiac disease causes problems in absorption and leads to steatorrhea, weight loss and diarrhea in adults as well as fatigue and a small build in children. One may suffer from pain and abdominal distension and symptoms such as iron deficiency anemia, massive chronic fatigue, long-standing migraine, peripheral neuropathy or tingling and numbness and pain, elevation in liver enzymes which is chronic and reduction in bone mass. Bone fractures are another problem, as is vitamin deficiency caused by a lack of B12 and folic acid. Late menstruation and early menopause are noted in women.
Other symptoms include infertility, dental enamel defects, anxiety, depression and dermatitis herpetiformis or itchy skin rashes. The silent celiac disease is also referred to as an asymptomatic celiac disease. Patients may not have the other symptoms, but still, experience villous atrophy damage to small intestines. Studies show that while patients thought they had not got any symptoms, once they leave gluten, they report improved health and reduction in acid reflux, abdominal bloating and screening reduces the likelihood of worsening of symptoms leading to 1 in 10 chances of developing the disease.
Numerous ways are there for this disease to impact patients. There is inadequate training in primary care residency programs, medical schools contributing to poor and low rates of diagnosis in the US. Currently, 80% of patients with this disease lack diagnosis.
According to Columbia University Medical Center’s Celiac Disease Center, those suffering from unexplained illness for a lot of months should consider celiac disease as a cause and be effectively screened for it. Additionally, first-degree relatives should be screened as they have 1 in 10 risks of development of celiac disease as against the general population risk of one in a hundred.
Certain people experience celiac diseases such as depression, foggy mind, ADHD type behavior, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, headache, bone and joint pain, diarrhea. Non-celiac gluten and wheat sensitivity refer to this condition while removing diet gluten causes symptoms to recede.
Celiac disease differs from food allergy as symptoms differ. Allergy to wheat can cause itching and watering in the eyes or difficulty breathing if one eats something with wheat in it. If one has celiac disease and eats a gluten-rich diet, intestinal problems like diarrhea, constipation or flatulence may result. Abdominal pain, anemia, nausea, itchy rash, loss of bone density or general fatigue or headaches or even bone or joint pain and mouth ulcers, weight loss and heartburn may result.
In children, intestinal problems are worse than for adults. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, bloating or belly swelling, GI symptoms, and weight loss. Some people have no problems, making diagnosis tougher. In those with celiac disease, inflammation leads to small intestinal mucosa when there is an intake of gluten. Celiac disease is a form of autoimmune disease with a genetic component.
Symptoms in adults include discomfort in the abdomen, bloating, nausea and bowel movement. A wide spectrum and range of symptoms can also take place. As intestine inflames, it loses its capacity for diet nutrient absorption leading to greater illness. Celiac disease requires no gluten. Celiac disease is also known as celiac sprue, gluten enteropathy, and nontropical sprue. Celiac disease which is also known as gluten-sensitive enteropathy is also known as coeliac and is an immune system reaction to consumption of the protein gluten.
Those with celiac disease, gluten triggers an autoimmune response in the small intestine. Across time reaction damages small intestine lining and leads to a lack of absorption of nutrients. Intestinal damage causes fatigue, weight loss, bloating anemia and diarrhea leading to a lot of complications. Malabsorption also impacts growth and development.
While there’s no cure for this disease, a strict gluten-free diet manages symptoms and promotes quicker healing of the intestine. Symptoms and signs of celiac disease vary and differ in adults and children. Most common sign of problems in adults are GI disturbances, fatigue, and weight loss as well as nausea and vomiting.
More than half of the adults with this disease have symptoms and signs not associated with the digestive system. Anemia results from iron deficiency, loss of bone density or softening of the bones called osteoporosis and osteomalacia respectively. Itchy dermatitis herpetiformis results too.
Damage to the dental enamel, mouth ulcers, fatigue, and headache as well as nervous system injury along with balance issues and cognitive impairments are noted in half of the adults who lack GI symptoms but have this disease. Additionally, there is joint pain, reduced spleen functioning, and heartburn as well as acid reflux.
Children under 2 years of age have certain symptoms and signs of celiac disease. Vomiting, chronic diarrhea, poor appetite, failure to thrive, lack of appetite and muscle wasting result. Older people have constipation, weight loss short stature, constipation and delayed puberty as well as learning disabilities and lack of seizures and muscle coordination.
Celiac disease is a massively serious condition leading to a host of negative symptoms including nutritional and digestive disturbance issues.
Photo by: CNX Open Stax/ CC BYMost Common Symptoms
Most common signs and symptoms of celiac disease are as follows.
#1 Diarrhea
Watery, loose stool is one of the key symptoms that most individuals experience before being detected with this disease. One study has found 79 percent of the diarrhea patients prior to treatment experience diarrhea. Post-treatment, just 17% of patients have chronic diarrhea.
Another study of 215 persons found diarrhea was a symptom of the untreated celiac disease. For a lot of patients, diarrhea was reduced within a couple of days of treatment. The time to resolve symptoms was within 4 weeks. Diarrhea is one of the most common symptoms of celiac disease. With treatment, the disease can be combated easily.
#2 Bloating
Bloating is a well-known symptom for patients who have celiac disease. This is because an inflammation results from consuming gluten-rich foods in the digestive tract, for those with this disease. The result is not just bloating, but other adverse digestive problems as well. A study of 1032 adults with the disease found bloating to be one of the most common symptom reported. Close to 73% of the people reported feeling bloated before being diagnosed with this condition. Another research found that when gluten was eliminated from the diet, people with this disease experienced relief from bloating.
#3 Flatulence
Excessive gases are a real digestive problem for those with celiac disease. In one study, gas was found to be a common symptom associated with gluten consumption for patients with celiac disease. Gas is one of the most common symptoms of this disease when patients are untreated.
#4 Tiredness
Falling energy levels and increased fatigue are some of the problems associated with celiac disease. A study of 51 patients with this disease found those untreated reported greater tiredness and fatigue-related problems. Those with sleep-related problems also report this disease. Fatigue also results because the untreated celiac disease causes small intestine damage, causing vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
#5 Loss of Weight
One of the most common symptoms of celiac disease is difficulty in keeping on the weight. The body’s ability to absorb nutrients is further impaired. This can lead to malnutrition and weight loss. Celiac disease has resulted in a lot of associated symptoms which cause weight loss too such as fatigue, stomach ache, and GI problems.
#6 Iron Deficiency Anemia
Celiac disease impairs nutrient absorption and leads to iron deficiency which can trigger lack of RBC or erythrocytes in the body or anemia. Symptoms of this form of anemia include chest pain, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, and headache. Research has also found that those with anemia are likely to face severe damage to the small intestine and low bone mass. There are many causes of iron deficiency anemia and celiac disease is one of the most impactful. It impairs nutrient absorption which leads to iron deficiency anemia.
#7 Lack of Regular Bowel Movement
Celiac disease can cause diarrhea in some individuals and constipation in others. Specifically, celiac disease harms the intestinal villi. These are small, finger type projections in the smaller intestine which absorb nutrients. With food traveling through the digestive tract, the nutrients are not effectively absorbed and absorb extra moisture. This affects the quality of the bowel movement.
#8 Depression
Along with the physical symptomatology, there are psychological factors that come into play as well. Depression is more common and severe in adults with celiac disease than the general population, according to research. Sticking to a gluten-free diet reduces chances of depression.
#9 Itching Rash
Celiac disease is commonly associated with dermatitis herpetiformis, an itching and blistering rash taking place on the glutes, knees or elbows. This rash is experienced by at least 17% of those with celiac disease and is a symptom associated with poor adherence to treatment. Some individuals may develop digestive symptoms that occur with celiac disease along with this rash.
Causes
Photo by: WikipediaProlific at English Wikipedia/ CC BYCeliac disease is also known as non-tropical sprue, celiac sprue, and gluten-based enteropathy. A hereditary and genetic autoimmune disease, it occurs when the person suffers an allergic reaction to protein gluten. This sensitivity damages the inner small intestine lining so nutrients cannot be absorbed from the food. Celiac disease is common throughout the western world and other eastern nations like Asia apart from Africa and South America.
The causes of celiac disease are genetic. It occurs when the villi which are finger type projections covering the small intestine are unable to absorb nutrients from food. How does this happen? The villi are covered with small, hair-like ending known as microvilli. These absorb the food’s nutrients. In those with celiac disease, the villi become flat or disappear due to allergies caused by eating gluten. The villi and microvilli are damaged, harming the lining of the small intestine.
Though celiac disease was once seen as a condition that commences in childhood, it is now believed this disease can take place at any age or time. One is susceptible if there is a medical history of celiac disease, there is type 1 diabetes, or there are autoimmune conditions like thyroiditis. Down syndrome and celiac disease are strongly linked. In older persons, celiac disease is triggered by infection of the intestine or intestinal conditions.
Apart from not being able to absorb nutrients from food, celiac disease patients also suffer deficiencies of vitamins and minerals. Lack of iron in the body due to malabsorption leads to anemia causing a reduction in RBC. This triggers tiredness and fatigue.
The food that is not absorbed is passed through bowel movements and irregular as well as constant constipation or diarrhea result. Additionally, those suffering from celiac disease cannot absorb the nutrients needed to eat from the food they have, and lack of minerals and vitamins lead to many different types of problems. Those who lack protein also suffer from swollen legs. Vitamin K deficiency causes bleeding gums, Additionally, some people may also face nerve damage and have difficulty thinking or focusing. Dry skin, sore tongue, and cankers on the lips or softening of the bones on account of the nutritional deficiencies result.
Modern testing procedures suggest that celiac disease may not result from typical intestinal symptoms. Anemia, liver malfunction or arthritis and infertility are also linked to celiac disease. Celiac disease occurs from an interaction between genes, consuming food with glutens as well as other environmental factors. The chief cause is not known. Infant feeding practices, gut bacteria, GI infections are other reasons for celiac disease.
Celiac disease can also be initiated and triggered post surgery, childbirth, severe emotional stress, pregnancy or even childbirth. Essentially, when the immune system of the body overreacts to gluten in the food, it damages the villi in the small intestine. So no matter how much you eat, you just cannot get the nutrients you need. Certain risk variations increase the chances of getting this disease. But those gene variants do not mean one will get celiac disease, which indicates additional factors must be involved. Around 1 percent of the population in Western countries is estimated to have celiac disease. It is common in many ethnicities and is found globally. Celiac disease is also a digestive disorder when it triggers immune system reaction to gluten.
Gluten is found in those food items made with barley, wheat, type, and triticale. It is also in oats and can even be found in certain vitamins, medicines, and makeup products. Gluten sensitivity or gluten intolerance results because the body cannot digest or break down the gluten. In celiac disease, immunity system’s reaction to gluten creates toxins that destroy the villi. These are small finger type protrusions that are within the small intestine. Once the villi are damaged, the body is not able to secure food nutrients it needs to grow, develop and remain healthy.
As per the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease, 1 in as many as 141 US residents have this disease. People with this disease cannot have gluten in their diet.
Risk Factors at Play
Celiac disease runs in families. As per the Chicago University Medical center, people have 1 in 22 chances of developing this disease if parents or siblings have this problem. Persons with other autoimmune diseases and specific genetic problems can also develop this disease. Autoimmune conditions associated with celiac disease include lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes of the type 1 type, thyroid disease, autoimmune liver disease, Sjogren’s syndrome, Addison’s disease, Turner and Down’s syndrome, lactose intolerance, intestinal lymphoma, and cancer.
Celiac disease can impact just about anyone. It is more common in those who have family members with this disease. Patients with type 1 diabetes, Turner or Down’s syndrome can also suffer from this condition. Autoimmune thyroid disease, microscopic colitis, Addison’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis are some of the other conditions associated with this disease.
Complications That Result
This disease, if not treated in time, can result in the following issues:
#1 Malnourishment
Damaged small intestines in patients with this disease cannot absorb nutrients. Malnourishment leads to weight loss and anemia. In children, the malnutrition can slow development and growth.
#2 Lack of Density of Bones and Calcium
Malabsorption of vitamin D and calcium can lead to bone softening or osteomalacia, brittle bones or rickets and low bone density or osteoporosis.
#3 Fertility Problems
Infertility and miscarriage are some of the biggest problems. There is malabsorption of calcium apart from which vitamin D also creates reproductive issues.
#4 Milk and Lactose Intolerance
A damaged small intestine can lead to diarrhea and stomach pain post ingestion of dairy products containing lactose. Once the intestine is healed, one can tolerate dairy products and eat non-gluten milk products. Some patients, however, experience lactose intolerance even after successful treatment of celiac disease.
#5 Cancer
For those with celiac disease who don’t follow a gluten-free diet, several forms of cancer can result such as small bowel cancer and intestinal lymphoma.
#6 Neurology Issues
Certain individuals with celiac disease can also develop neurological issues like seizures, peripheral neuropathy and diseases pertaining to neural networks in the hands and limbs. In children, celiac disease can also cause an initial delay of puberty, loss of weight, irritability, anemia, epilepsy, enamel defects and arthritis.
Non-responsive Celiac
This is a disease which at least 30 percent of patients with this disorder suffer from. A response to a gluten-free diet is beneficial. This condition called nonresponsive celiac disease comes about due to dietary contamination with gluten. Working with a dietitian is needed.
Those suffering from the non-responsive celiac disease may have conditions such as bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine, poor pancreatic function, microscopic colitis, IBS or lactose, and fructose intolerance or even refractory celiac disease can impact the body.
Refractory Celiac Disease
In rare cases, intestinal injury of the celiac disease leads to considerable malabsorption, though a gluten-free diet is followed, and this is called refractory celiac disease. If signs and symptoms of the disease persist following a gluten-free diet, for 6 months to one year, doctors may recommend testing and search for explanations for symptoms. Doctors can also recommend treatments with steroids to lower intestinal swelling or medication that suppresses the autoimmune response. Patients with celiac disease should monitor their treatment response for an impact.
How Gluten Intolerance Causes Complications
A protein called gluten releases an enzyme, tissue transglutaminase that changes the protein into a chemical triggering an autoimmune response. It further exacerbates the lining of the small intestine. Additionally, normal intestinal villi are destroyed so nutrients are not effectively absorbed by the body. This malabsorption damages other bodily organs such as the liver, brain, and bone which depend on nutrients to normal function. Lack of effective nutrition leads to lack of growth and development in children too.
Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
When the diagnosis is to be made, a 2 stage screening process leads to a better diagnosis. Blood test for immunoglobulin A anti-tissue TTG or transglutaminase antibody is one step. If the blood test for screening yields a positive result, the first part of the small intestine, namely the duodenal lining undergoes endoscopy and biopsy. This is performed under anesthesia, as a fiber optic tube passes through the mouth to the esophagus and small bits of tissue are microscopically examined.
The patient needs to eat a regular diet for some weeks prior to the screening. If a gluten-free diet commences, the test could return a false negative. Once the diagnosis is carried out, appropriate screening for osteoporosis is carried out. As it is familial, once a person is diagnosed with celiac disease, others in the family should also be screened for it. Many suffering from celiac disease never realizes they have it, with less than 20% of the disease ever getting a correct diagnosis. The intestinal damage is slow and symptoms are varied. It is years before the diagnosis is made.
Doctors use blood tests to help assess if one has celiac disease. While certain antibodies are searched for through serology tests, genetic testing for human leukocyte antigens is needed to ensure a false diagnosis is not made. When blood testing for the disease is positive, endoscopy needs to be carried out. In this procedure, the small intestine tissue can be examined to check if it is damaged.
For diagnosing celiac disease, tests will be conducted and questions will be asked about symptoms and their relationship to food. These include blood tests and small intestine examination by taking an intestinal tissue sample. Blood tests also consider antibodies produced by patients are higher than average. Antibodies are an indication that gluten is being erroneously assumed to be a foreign substance which must be removed from the human body. A thin tube, the endoscope, is inserted into the intestine. The tissue sample of the small intestine lining is examined to see if cells show signs of the disease.
Treatment
To manage celiac disease, patients must avoid gluten-containing food. This means one cannot eat bread products or those composed of rye, wheat or barley. Gluten is also found in pasta. Oats are another factor to avoid. Oats themselves do not have gluten but can be contaminated while being processed.
Those with celiac disease have to check labels of processed food items for gluten. Processed food should not be purchased until people know exactly what’s in it. Care should also be taken if medicines and vitamins contain gluten. More gluten-free options are available. Ensuring that the body is hydrated is important. Vitamin and mineral supplements can solve the problem of malabsorption. As a person follows a gluten-free diet, the healing of the bowels becomes faster and the issue of malabsorption may disappear.
It can be tough to follow a completely gluten-free diet. Definitive diagnosis of celiac disease is therefore important. In case the celiac disease is diagnosed, gluten-free diets should be followed across life. Some persons find it helpful to consult a nutritionist to adopt a gluten-free diet.
Presently, there are no drugs to treat this disease. Strict gluten-free diet is needed. In addition to moving away from the cake, bread, and other baked goods, you need to avoid pasta, cereals, beer and toothpaste, medicines and other gluten-containing products.
For those suffering from severe nutritional deficiencies, doctors may take gluten-free vitamins and mineral supplements and prescribe medicines in the event of a skin rash. Once you have followed a gluten-free diet for weeks, the small intestine begins to heal and feel better.
Celiac diseases run in families as these are genetic disorders. If you have parents, brothers, sisters or children with celiac disease, there is one in ten chances of getting it oneself. Having the genetic predisposition for celiac disease does not mean you will develop this disease.
A stressful event such as viral infections, surgeries or emotional traumas can initiate it. It can also take place post pregnancy. Eating foods with gluten may harm such a person. The disease is common among those with Turner syndrome, Down syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis, among others.
Researchers estimate close to 20% of persons with celiac disease may get a diagnosis. Doctors also order two blood tests for diagnosing celiac disease symptoms. Through serology testing, it has elevated levels of antibody protein indicating immune system reaction to gluten. Additionally, genetic testing for human antibodies leukocyte antigens HLA-DQ2 and DQ-8 can be used to check out whether a person has celiac disease.
Results of the test indicate celiac disease and common blood tests include CBC or complete blood count, cholesterol test, liver function test, alkaline phosphatase level test and serum albumin test. In those with dermatitis rash, skin biopsies can help in diagnosing celiac disease and internal biopsies may not even be needed. In the event of blood test or skin biopsy, an upper endoscopy can be used for testing celiac disease.
Therefore, the only means of treating celiac disease is to remove gluten from the diet. This permits the healing of intestinal villi for healing and absorbing nutrients effectively. The doctor can enable you to teach how to avoid gluten and identify ingredients that contain this protein. Symptoms are eliminated within days of removing gluten from the diet. Gluten should not stop being eaten till diagnosis is carried out. Removal of gluten on a permanent basis is advisable.
Food Precautions to Take
Maintaining a gluten-free diet is all about being alert about the food being eaten. Many companies are making zero gluten foods found in specialty food stores. For those with this disease, it is essential to know how foods should be safe. Numerous food guidelines can help you to assess what to eat and how to avoid the ingredients that spell trouble.
Foods with ingredients like semolina, graham flour, farina, durum, bulgur, triticale, barley, rye, spelled and wheat are not advisable. Unless the label says it’s gluten-free, don’t opt for baked goodies like cakes, pies, cookies, and crackers. Avoid candy, beer, bread, croûtons, gravies, imitation mutton or chicken or seafood and oats. Give a wide berth to self-basting poultry, pasta, processed lunch meats, hot dogs, sausages, sauces, salad dressings and soups that are rich in gluten too.
If you need zero-gluten starch in your diet, check out corn, amaranth, buckwheat, arrowroot, cornmeal, flour composed of rice, corn, soy, potatoes or beans, pure corn tortillas, rice, tapioca, and quinoa. Gluten-free foods include not marinated, nonbreaded and no coating fresh meats and fish. Fruits, most dairy products that are gluten-free and starchy veggies like potatoes and peas are also a good idea. Go for rice, lentils, beans, and veggies. Additionally, you can opt for wine, spirits, ciders and distilled liquors.
Symptoms can improve within just days of making dietary adjustments. In children, intestines heal in 3-6 months. Intestinal healing occurs in adults after several years. Once the small intestine heals, the body is able to absorb nutrients correctly. Lifelong, gluten-free diets are the only way to handle celiac disease. Along with wheat, foods that are rich in gluten include barley, bulgur, malt, rye, and many such items.
Photo by: AmazonCheck out a dietitian to guide you about the right kinds of foods to eat. Once gluten is removed from the diet, inflammation in the small intestine lessens. Within a few weeks, the patient will begin to feel better and villi may even regrow within a couple of months. Healing within the small intestine takes place faster in children than adults.
If a product that contains gluten is consumed, abdominal pain and diarrhea may result. Symptoms or signs of the disease may be experienced after eating gluten, but even trace elements of this protein in the diet of those with celiac disease can be dangerous. Hidden gluten is also present in medications, foods and non-food products such as modified food starches, food stabilizers, and preservatives. OTC medications and prescription, vitamin, and mineral herbal and nutritional supplements, makeup products like lipsticks, and even stamp and envelope glue contain gluten. Toothpaste and mouthwashes also contain this product.
If one has severe nutritional deficiencies, the doctor or dietitian may suggest supplementation. Calcium, folate, iron, vitamins D, K and B-12 as well as zinc are used. Vitamins, as well as supplements, are taken in the form of pills. If there is a problem in absorbing vitamins, injections are the way.
Follow Up Treatment
For those with this disease, follow up visits and treatments are essential to ensure a gluten-free diet. Doctors also need to check that support is provided for maintaining the diet for life. Blood tests can be used for monitoring treatment responses as well. Results indicate when you have attained freedom from this disease, once you opt for a zero gluten diet for 6-12 months. IN
the event that test results are positive, doctors need to find the reason which includes unintentional exposure to dietary gluten.
The tests are not perfect and in the event that results are not positive, it is possible that gluten may be part of the diet and continue to cause symptoms and damage the intestines. For those who want to have symptoms or recur, one needs a follow-up endoscopy with biopsies to ensure healing takes place. Adults have a wider need for follow-ups although pediatric patients may require it as well. Certain doctors recommend routine re-biopsy for those diagnosed in adulthood, as the rate of healing is not certain.
Follow-ups with expert dietitians for maintaining zero gluten diet is a must.
Medications to Contain Intestinal Swelling
If one has a severely damaged small intestine, steroids need to be in place to control the inflammation. Steroids can lead to severe symptoms and signs of celiac disease as the intestine heals. For those with skin rash, medication to control the dermatitis herpetiformis may be recommended, such as dapsone, besides a zero gluten diet.
No Proven Cure for Refractory Disease
For those with the refractory celiac disease, severe symptoms may result. Or symptoms may lessen and the relapse. However, the small intestine does not heal. For refractory celiac disease, there is no treatment. Those with the refractory celiac disease may continue to have the severity of symptoms or if symptoms lessen and then relapse may occur, there can be complications. Those with the refractory form of this disease should be treated by the experts. Several causes are there for this condition. Doctors can use steroid therapy such as systemic steroids like prednisone or topical budesonide. Same medications can be used to treat a wide variety of related conditions.
Future Treatments
While the only proven treatment for this disease is a gluten-free diet, there are no guarantees. Several treatments are being tried out to develop a cure for this disease. While some bind or neutralize the gluten, others block the leaky gut the gluten triggers addressing the intestinal barriers. Yet others target the immune system of the body. While researchers have been trying to modify wheat, there is no success as of now.
A lot of treatments are in place for developing celiac disease. But none of these treatments will be approved any time soon.
Home and Lifestyle Remedies
Photo by: AmazonIf one is diagnosed with celiac disease, all foods containing gluten need to be avoided. Referrals are essential to a dietary expert so you can be clear how to avoid gluten. Vitamins, nutrients, fibers, and calcium in the diet are essential for averting a problem. While this disease is a lifelong condition with zero cures, symptoms can be managed by adhering to a zero gluten diet. Products containing wheat, spelled, barley or rye must be avoided. Foods that have undergone cross-contamination must be avoided too.
While processed foods should be avoided, healthy fats are the best choice. Go for nuts, legumes, and good cholesterol fats. A gluten-free diet can transform the health of those with this disease. Quinoa, tapioca, corn — the list of dietary intake that can preserve gluten-free forms and yet offer healthy carb and starch content are many. While gluten has substitutes like carob, research on this matter is still forthcoming.
No proven treatments are there though enzyme therapies are recommended by some. Following a gluten-free diet can be hard. Make it easy by getting educated, following doctor recommendations and finding a support group. Gastroenterologists can also prove beneficial in guiding you about the treatment course. Some common questions you need to check with the doctor is whether you have regular, silent or refractory celiac disease, the likely symptom reasons, tests required, treatments that can help and dietary restrictions that need to be followed. Check regarding the foods that contain gluten and study the best diet with the help of a dietary consultant.
Conclusion
Gluten is a complex protein with a range of effects for those with celiac disease. You need to work hand in hand with your doctor to bring about effective management of the symptoms. Don’t be a victim of this disease. Make yourself aware and get tested, so that you can access the treatment you need and avert serious diseases or complications associated with this condition.